目前在WPF中使用Multi-touch功能,必須透過P/Invoke的方式呼叫Win32 Touch API的功能(可參考這篇文章 : WPF + Windows7 Multi-touch (Part 2) ), 或是可以直接使用微軟提供的Windows 7 Multitouch .NET Interop Sample Library, 它提供 WPF 與 WinForms 3.5 SP1 要開發Multi-Touch 程式所需的功能, 不過利用上述這些方法開發觸控功能時, 還是有稍嫌複雜, 也不是很直覺.
因此在WPF 4.0 已經將一些觸控功能放到UIElement, UIElement3D和ContentElement中,
在 Beta 1中, 將支援高階操作的觸控功能(Manipulation), 如下所示:
因此在WPF 4.0 已經將一些觸控功能放到UIElement, UIElement3D和ContentElement中,
在 Beta 1中, 將支援高階操作的觸控功能(Manipulation), 如下所示:
- ManipulationStarted
- ManipulationDelta
- ManipulationInertiaStarting
- ManipulationCompleted
- ManipulationBoundaryFeedback
而在Beta 2 中, 除了原本高階操作的觸控功能(Manipulation)外, 還提供的Touch相關的event,如下所示:
下面我們將利用WPF 4.0 Beta2 Touch功能, 撰寫一個顯示目前觸控點的應用程式, 其步驟如下:
軟體和硬體需求
XAML檔的部份:
C#檔的部分:
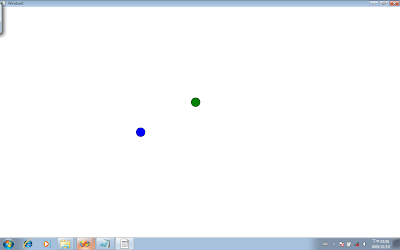
顯示結果如下所示:

[圖 1] Multi-touch points in WPF4.0 Beta 2
不過目前這些觸控功能在Beta版還是有很多bug, 可參考這些文章測試出來的結果:
Multi-touch in WPF4.0 Beta2
WPF 4, Beta 2 expands multi-touch API but is buggy
參考文章:
Windows 7: Experimenting with Multi-Touch on Windows 7 ( Part 5 )
Windows using Multi-touch using WPF
Multi-touch in WPF4.0 and VS2010
Introduction to WPF 4 Multitouch
Walkthrough: Creating Your First Touch Application
What's New in WPF Version 4
- PreviewTouchDown
- TouchDown
- PreviewTouchMove
- TouchMove
- PreviewTouchUp
- TouchUp
- GotTouchCapture
- LostTouchCapture
- TouchEnter
- TouchLeave
下面我們將利用WPF 4.0 Beta2 Touch功能, 撰寫一個顯示目前觸控點的應用程式, 其步驟如下:
軟體和硬體需求
- IDE -安裝Visual Studio 2010 Beta 2
- OS 版本 - Windows 7 Ultimate Editions
- 硬體設備 - 準備一台具有多點觸控的螢幕或電腦
XAML檔的部份:
<Window x:Class="WPFTouchPoint.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="MainWindow" Height="800" Width="800"
TouchDown="Window_TouchDown"
TouchMove="Window_TouchMove"
TouchUp="Window_TouchUp">
<Canvas Background="Black">
<Ellipse
Canvas.Left="0"
Canvas.Top="0"
Name="Touch1"
Stroke="Black"
Height="60"
Width="60"
Fill="LightGreen"
Visibility="Hidden">
<Ellipse.BitmapEffect>
<DropShadowBitmapEffect ShadowDepth="10"
Direction="270"
Color="White"
Opacity="0.5"
Softness="0.25"/>
</Ellipse.BitmapEffect>
</Ellipse>
<Ellipse
Canvas.Left="0"
Canvas.Top="0"
Name="Touch2"
Stroke="Black"
Height="60"
Width="60"
Fill="LightBlue"
Visibility="Hidden">
<Ellipse.BitmapEffect>
<dropshadowbitmapeffect shadowdepth="10" direction="270" color="White"
opacity="0.5" softness="0.25">
</dropshadowbitmapeffect>
</Ellipse>
</Canvas>
</Window>
C#檔的部分:
namespace WPFTouchPoint
{
///
/// Interaction logic for MainWindow.xaml
///
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
private int Touch1ID = 0; // id for first touch contact
private int Touch2ID = 0; // id for second touch contact
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Window_TouchDown(object sender, TouchEventArgs e)
{
TouchPoint p = e.GetTouchPoint(this);
if (Touch1ID == 0)
{
// Show the touch point
Touch1.Visibility = Visibility.Visible;
Touch1ID = e.TouchDevice.Id;
// move the ellipse to the given location
Touch1.SetValue(Canvas.LeftProperty, p.Position.X - Touch1.Width / 2);
Touch1.SetValue(Canvas.TopProperty, p.Position.Y - Touch1.Height / 2);
}
else if (Touch2ID == 0)
{
Touch2.Visibility = Visibility.Visible;
Touch2ID = e.TouchDevice.Id;
// move the ellipse to the given location
Touch2.SetValue(Canvas.LeftProperty, p.Position.X - Touch2.Width / 2);
Touch2.SetValue(Canvas.TopProperty, p.Position.Y - Touch2.Height / 2);
}
}
private void Window_TouchMove(object sender, TouchEventArgs e)
{
TouchPoint p = e.GetTouchPoint(this);
// determine which contact this belongs to
if (Touch1ID == e.TouchDevice.Id)
{
Touch1.SetValue(Canvas.LeftProperty, p.Position.X - Touch1.Width / 2);
Touch1.SetValue(Canvas.TopProperty, p.Position.Y - Touch1.Height / 2);
}
else if (Touch2ID == e.TouchDevice.Id)
{
Touch2.SetValue(Canvas.LeftProperty, p.Position.X - Touch2.Width / 2);
Touch2.SetValue(Canvas.TopProperty, p.Position.Y - Touch2.Height / 2);
}
}
private void Window_TouchUp(object sender, TouchEventArgs e)
{
if (e.TouchDevice.Id == Touch1ID)
{
Touch1.Visibility = Visibility.Hidden;
Touch1ID = 0;
}
else if (e.TouchDevice.Id == Touch2ID)
{
Touch2.Visibility = Visibility.Hidden;
Touch2ID = 0;
}
}
}
}
顯示結果如下所示:

[圖 1] Multi-touch points in WPF4.0 Beta 2
不過目前這些觸控功能在Beta版還是有很多bug, 可參考這些文章測試出來的結果:
Multi-touch in WPF4.0 Beta2
WPF 4, Beta 2 expands multi-touch API but is buggy
參考文章:
Windows 7: Experimenting with Multi-Touch on Windows 7 ( Part 5 )
Windows using Multi-touch using WPF
Multi-touch in WPF4.0 and VS2010
Introduction to WPF 4 Multitouch
Walkthrough: Creating Your First Touch Application
What's New in WPF Version 4